Executive Summary
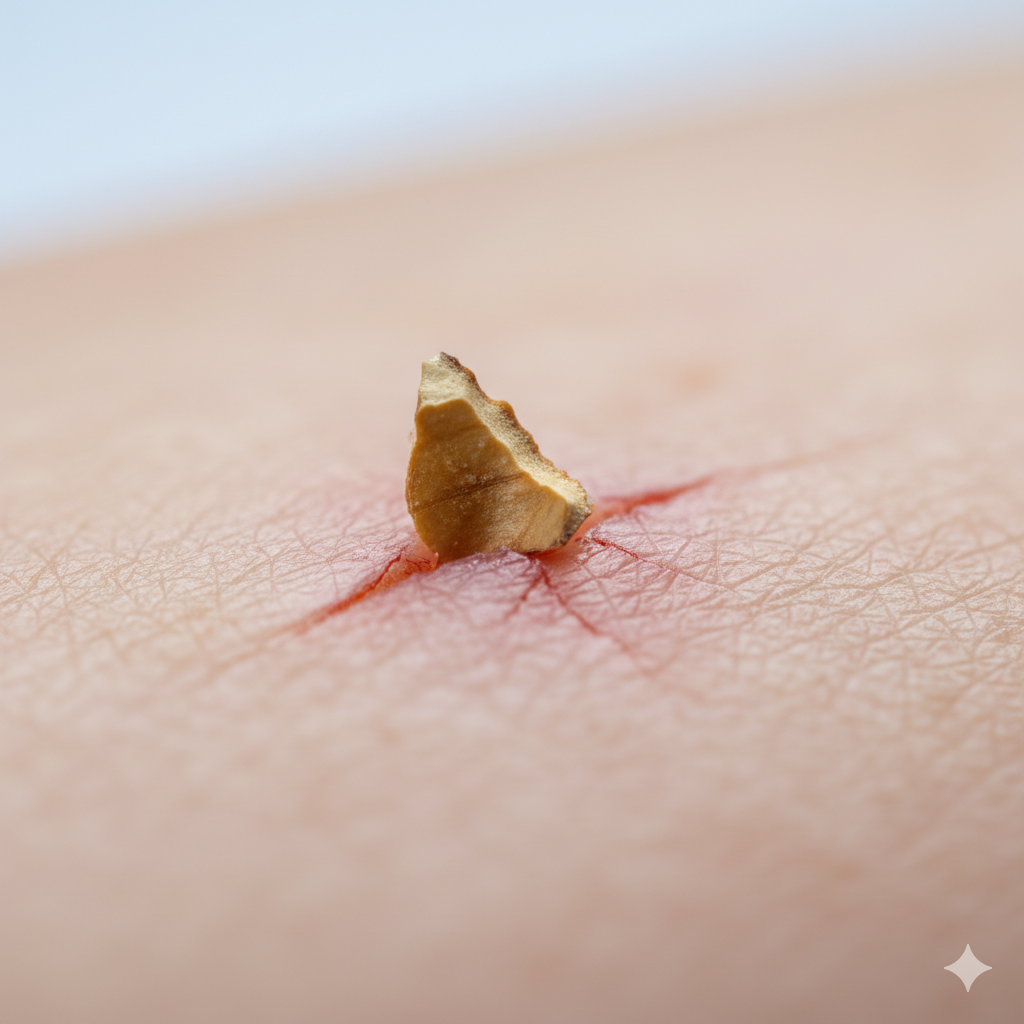
This report provides a clinical analysis of the safety and efficacy of physical exfoliating scrubs, with a specific focus on products containing crushed walnut shells. It examines the mechanics of exfoliation, the physiological impact on the skin, and critically, how the frequency of use dictates the dermatological outcome. The key findings indicate that while marketed as “natural,” crushed walnut shells are an inherently abrasive ingredient with jagged, sharp particles that can create microscopic tears in the skin. This damage compromises the skin’s protective barrier, leading to increased water loss, inflammation, sensitivity, and a higher risk of infection.
A central argument of this report is the dose-response relationship between exfoliation frequency and skin damage. Using an abrasive scrub at the recommended frequency (1-3 times per week) already carries risks, particularly for sensitive skin. Moderate overuse (near-daily) leads to a state of chronic barrier compromise, identifiable by persistent redness, dryness, and a deceptive “waxy” shine. Severe overuse (multiple times daily) pushes the skin into a pathological state, triggering chronic inflammation, premature aging (“inflammaging”), and compensatory oil production that can lead to severe acne.
Based on these findings, this report strongly recommends avoiding crushed walnut shell scrubs for facial use. Safer, more effective alternatives are readily available, including well-formulated chemical exfoliants—such as Alpha-Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) and Beta-Hydroxy Acids (BHAs)—which offer controlled, uniform exfoliation without mechanical injury. For those who prefer physical exfoliation, products with verifiably smooth, spherical particles like jojoba beads are the only recommended safe alternative. Ultimately, the report concludes that skin health is best supported by gentle, evidence-based interventions and moderation, rather than aggressive abrasion.
(more…)